Finding low-competition keywords with high traffic is one of the most effective ways to grow organic traffic without going head-to-head with established competitors. Instead of chasing after highly competitive keywords that require strong domain authority and thousands of backlinks, low-competition keywords allow you to rank faster with less effort and fewer resources.
This guide provides a complete step-by-step breakdown of how to find low-competition, high-traffic keywords, validate them using search intent, and leverage them to increase visibility and traffic. We’ll also explore advanced strategies like content gap analysis, competitor insights, and keyword clustering.
You’ll learn practical methods to identify opportunities others overlook, and how to transform these insights into SEO-optimized content that builds topical authority. Whether you’re a blogger, niche website owner, or part of a growing brand, these techniques will help you drive sustainable, long-term traffic. From tools to tactics, this article brings data-backed strategies that align with modern search behavior and semantic SEO principles.
What Are Low-Competition Keywords?
Low-competition keywords are search terms that have relatively fewer pages trying to rank for them, making it easier for new or less authoritative websites to appear on the first page of search results.
Unlike high-competition keywords dominated by top-ranking sites, low-competition terms offer a more achievable entry point. These keywords typically have moderate to high search volume and lower keyword difficulty scores in tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Ubersuggest.
Search engines consider many factors when ranking content, such as backlinks, content quality, and topical authority. For newer sites or niche publishers, targeting low-competition terms offers the best chance to break through and get indexed quickly.
Often, these keywords are overlooked by larger players because they focus on broader or more lucrative terms. But with the right content and optimization strategy, they can bring substantial and steady traffic, especially when grouped into clusters.
Why Are Low-Competition Keywords Important?
They are essential for accelerating your SEO growth without needing heavy investments in backlinks, authority, or time.
Most small websites face the challenge of competing with top brands that dominate popular keywords. Low-competition keywords solve this by allowing you to bypass heavily contested spaces. They offer a realistic path to the top of the SERPs even if your domain is relatively new or lacks backlinks.
These terms are often found in long-tail or question-based formats, which Google favors for delivering highly specific and intent-matched results. According to Backlinko, long-tail keywords make up over 70% of all searches, meaning there’s a significant pool of untapped traffic available.
Moreover, Google’s shift toward semantic understanding and user intent rewards content that answers precise queries. Low-competition keywords are more likely to match these searches, improving both your click-through rate and dwell time.
By consistently targeting and ranking for low-competition terms, you build topical authority in your niche. Over time, this gives you a stronger foundation to compete for broader and more competitive terms later on.
Step-by-Step Process to Find Low-Competition Keywords
The keyword research process involves building, expanding, filtering, and validating your keyword ideas with a balance of volume and difficulty in mind. Below is a systematic approach that uses both manual techniques and keyword research tools to discover real opportunities.
Step 1: Build Your Initial Keyword List

Start by brainstorming a seed list of topics that relate to your niche or industry. These seed keywords act as the foundation for expanding into more targeted terms.
For example, if your niche is “fitness for beginners,” seed terms could be “beginner workouts,” “easy fitness routines,” or “weight loss for new moms.” Think about problems your audience faces, and what they would type into search engines.
Use Google autocomplete to uncover variations. Just typing your seed keyword into the search bar and looking at what Google suggests can reveal popular phrases with real user intent. Scroll down to “related searches” as well to collect more ideas.
Reddit threads, Quora questions, niche forums, and YouTube comments are also excellent sources for natural language phrases. These platforms expose how your audience asks questions and expresses intent, which is key for finding untapped keywords.
Step 2: Expand Your Keyword Ideas Using Keyword Research Tools
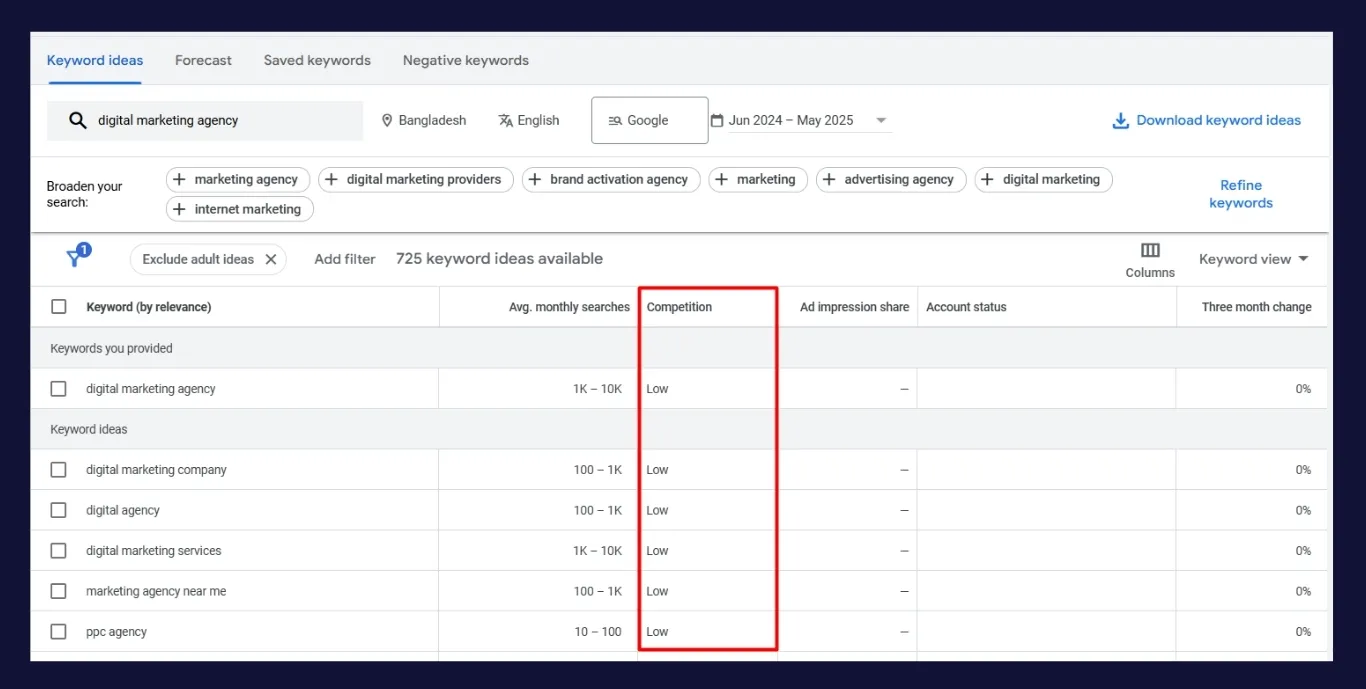
Once you’ve gathered an initial list, use tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, Ubersuggest, or KeywordTool.io to broaden your keyword scope.
Enter your seed terms to generate a list of related keywords. Most tools will provide search volume, keyword difficulty, CPC, and competition data. Filter these based on your priorities usually low difficulty (under 30 KD) and decent volume (500+ searches per month).
Look at the “Questions” or “Phrase Match” sections in tools, as they often contain long-tail variants with clearer intent and lower competition. Google Search Console (for existing websites) also provides insights into the keywords you’re already appearing for but not yet ranking on page one.
The key is to look for patterns: keywords with steady volume, commercial or informational intent, and weak competition.
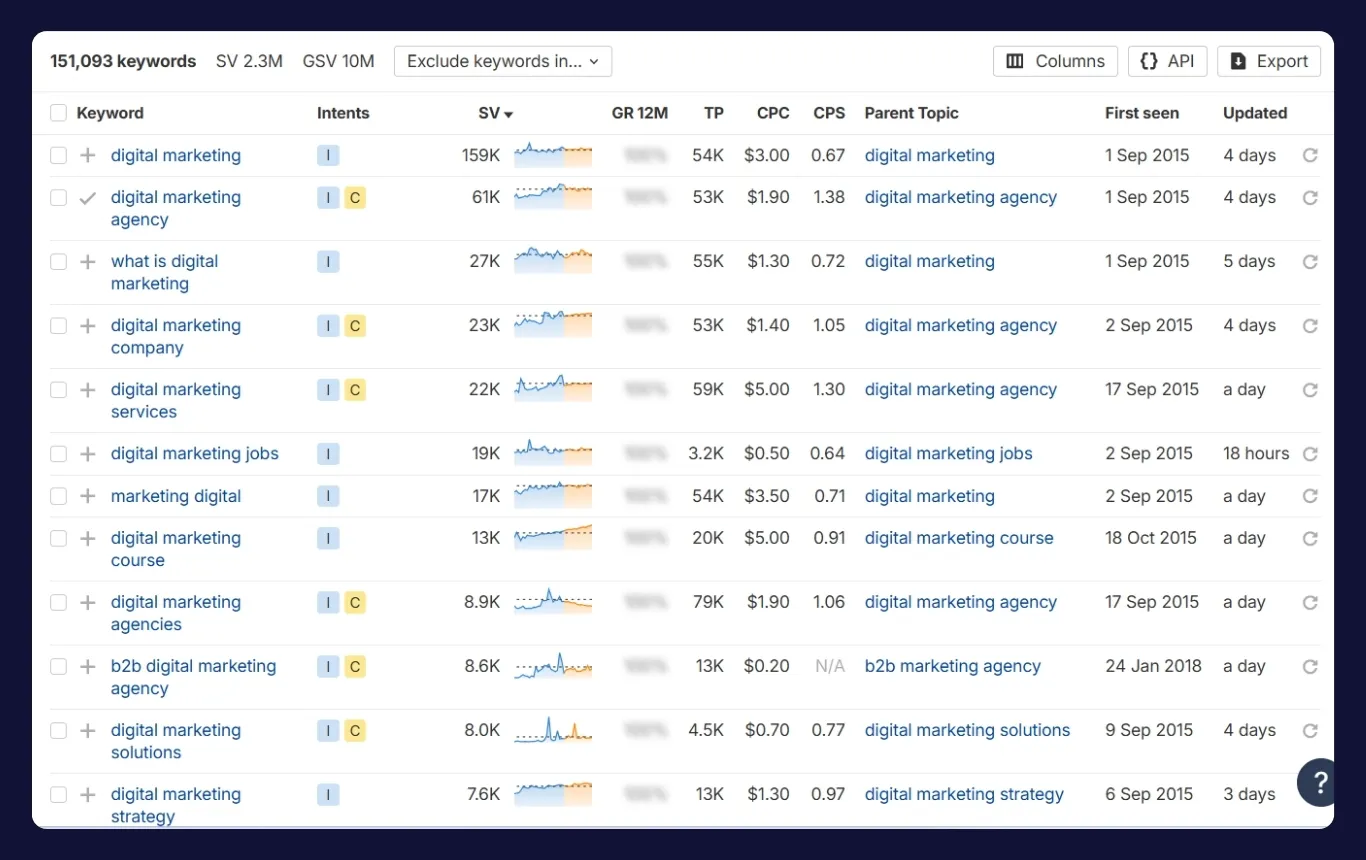
Step 3: Filter for High-Search Volume, Low-Competition Keywords
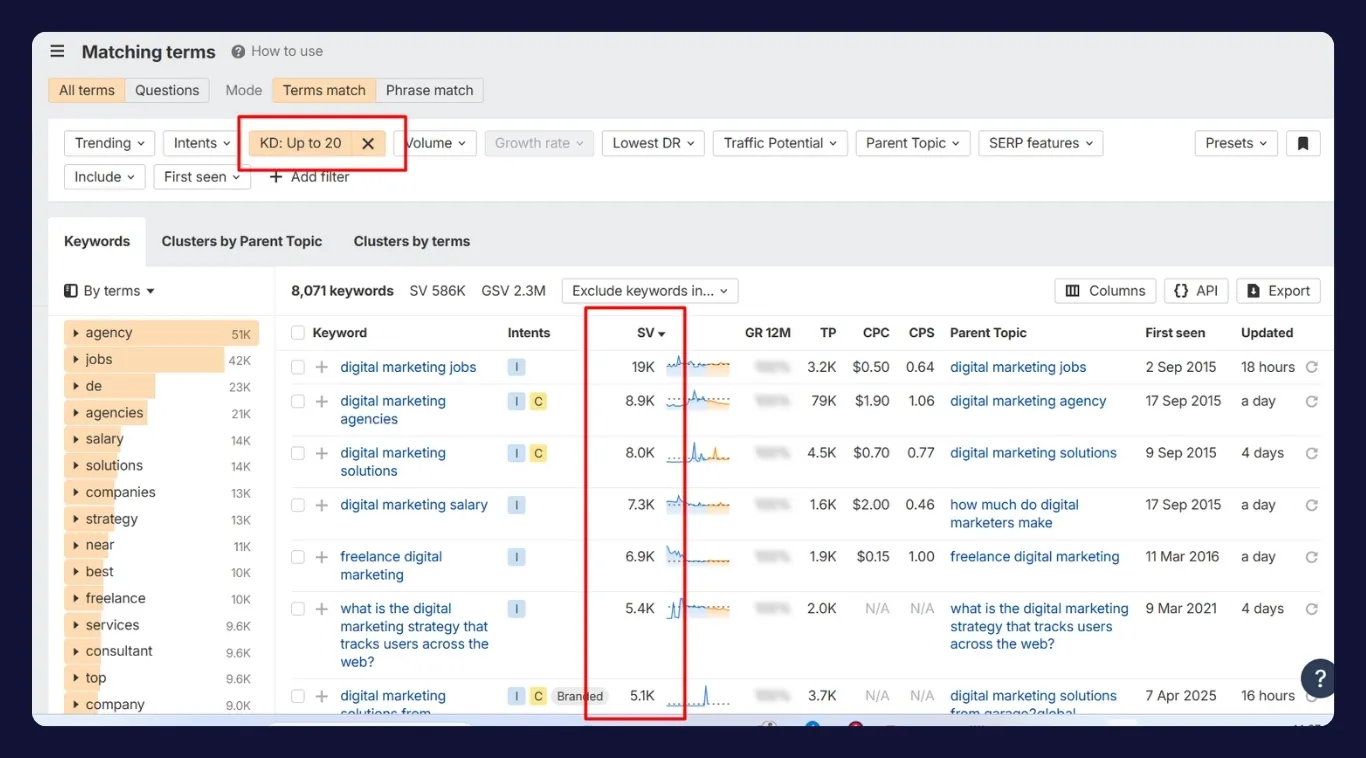
Volume alone isn’t enough. To qualify as a low-competition keyword, the term must have fewer strong competitors in the top search results.
Keyword tools assign difficulty scores using backlink profiles, domain ratings, and content strength of ranking pages. Use these scores as a guide, but always verify by manually checking the SERP.
Look for signs of weak competition such as:
- Forum threads (e.g., Reddit, Quora) ranking on page 1
- Outdated or thin content
- Low-authority domains ranking in the top 3 positions
- Pages without backlinks or structured formatting
According to Ahrefs, even a keyword with a difficulty score of 20 might be harder if the top pages are well-optimized. So always cross-check with the actual results and not just the tool data.
Step 4: Analyze Search Intent to Validate Opportunities
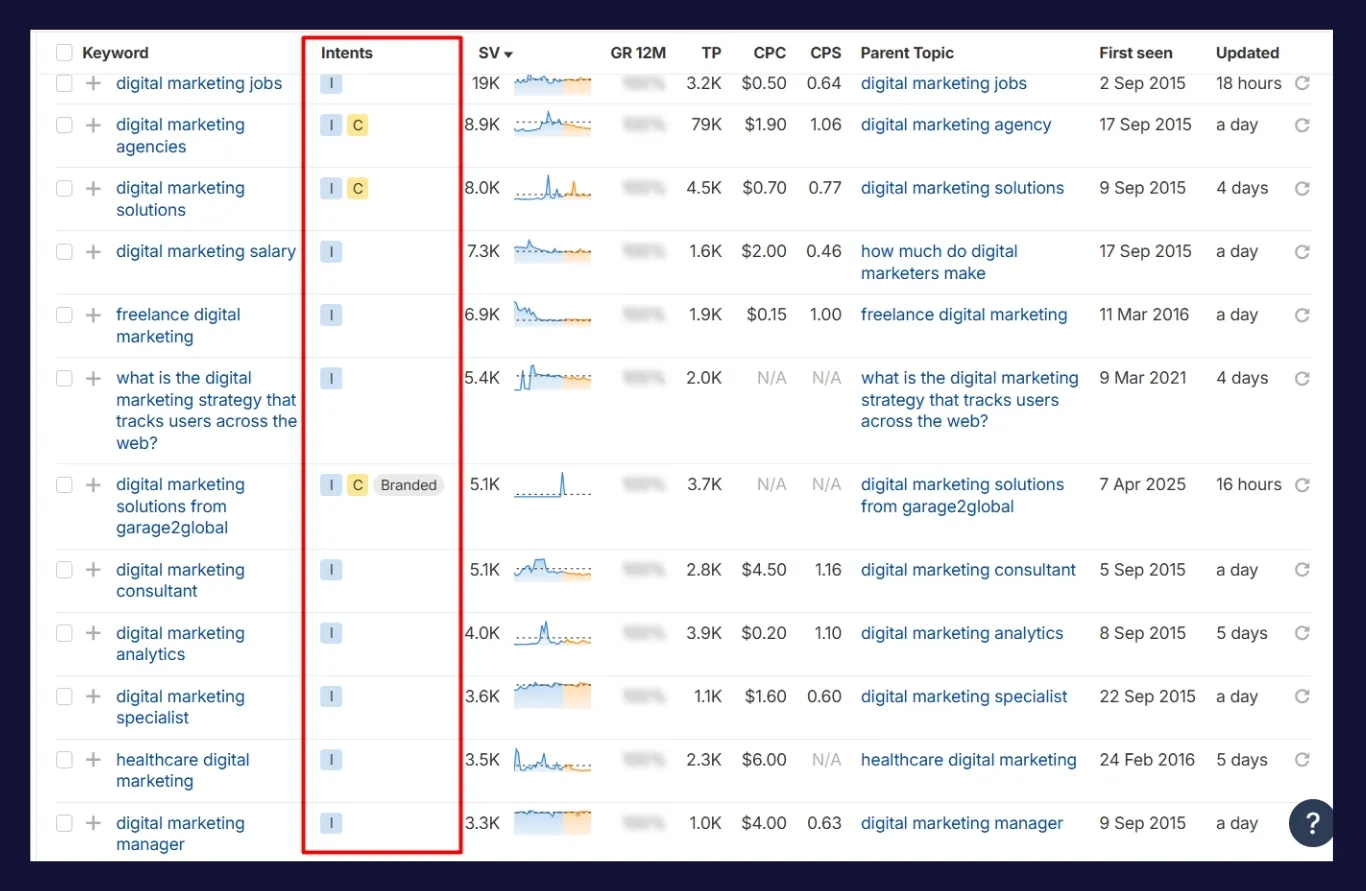
Search intent tells you why someone is making a query whether they’re looking for information, trying to buy something, or comparing options.
Google is now intent-focused. If your content doesn’t match the intent behind a keyword, it won’t rank even if it’s well-written.
There are four main types of search intent:
- Informational: The user wants to learn something
- Navigational: The user wants to find a specific site
- Transactional: The user is ready to buy
- Commercial investigation: The user is comparing before buying
Analyze the top 10 results for your chosen keyword. Are the pages blog posts, product listings, or comparison guides? Match your content format to what’s already ranking. This ensures you’re aligning with what Google has determined is the most relevant result type.
Also look at “People Also Ask” and “Related Searches” sections to identify other questions users have around that keyword. These can help strengthen your content’s relevance and depth.
Step 5: Assess Keyword Difficulty and Competition Level
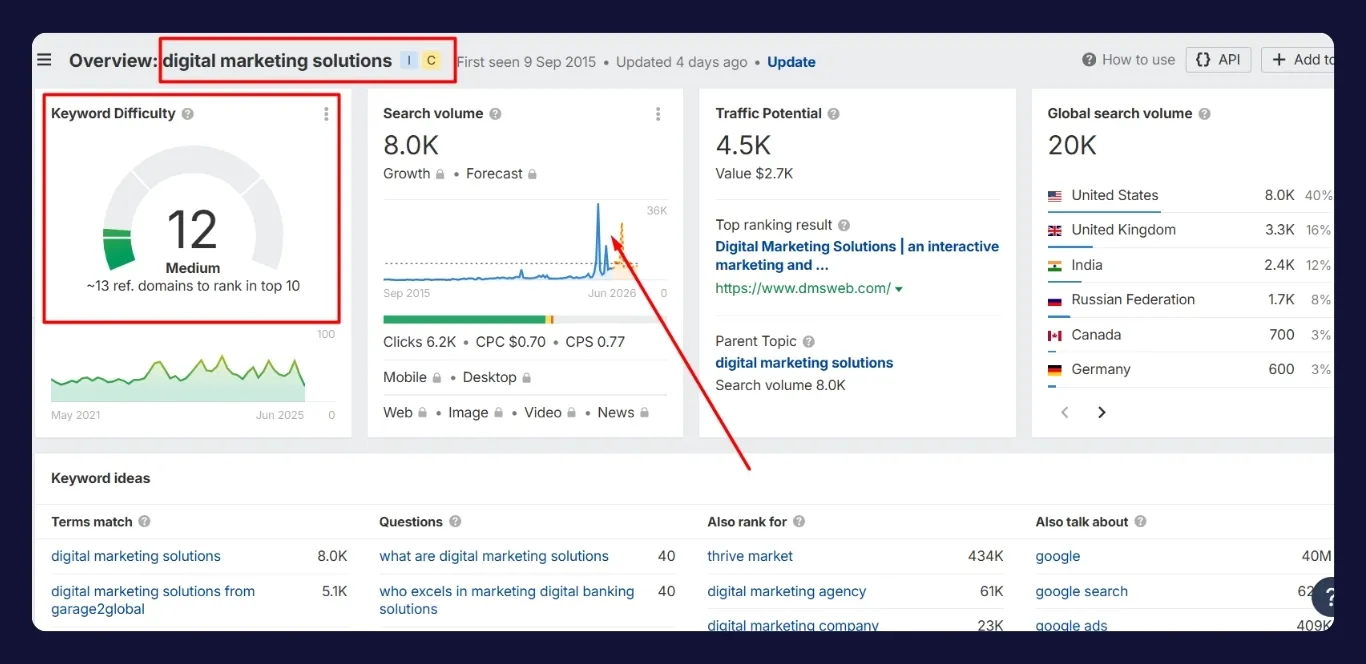
The final validation step is understanding how hard it will be to rank.
Keyword difficulty scores are just one part. Look at backlink counts, content depth, page experience, and domain authority of ranking pages. Use SEO plugins like Ahrefs Toolbar or MozBar to analyze competitors in the SERP quickly.
Check if the top-ranking pages are well-structured, answer search intent clearly, and cover the topic comprehensively. If you find that these results are shallow or outdated, that’s your opening.
Content with strong on-page SEO, semantic depth, internal linking, and topical authority can outrank weaker pages even if they have more backlinks.
Advanced Strategies for Finding Low-Competition Keywords
Beyond traditional keyword research, there are strategic methods that uncover hidden keyword opportunities competitors often overlook. These advanced techniques rely on analyzing gaps, leveraging long-tail formats, and understanding how search engines interpret entities, context, and relevance.
Leverage Content Gap Analysis to Identify Missed Opportunities
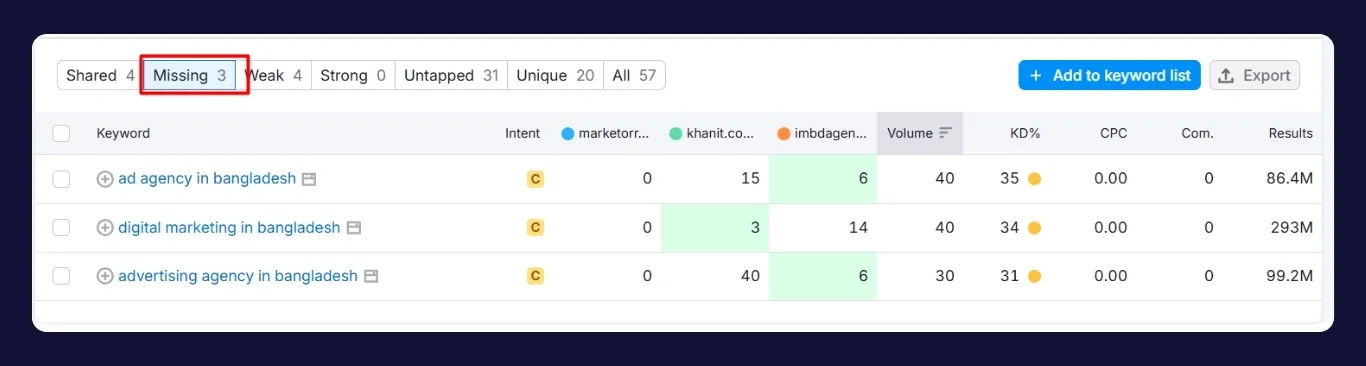
Content gap analysis reveals the keywords your competitors rank for but you don’t. This uncovers untapped queries that are already proven to generate traffic in your niche.
Start by selecting 3 to 5 top competitors in your space. Use tools like Ahrefs’ “Content Gap” feature or SEMrush’s “Keyword Gap” to compare your site with theirs. These tools show you the keywords that appear on competitor pages but not on yours.
Pay special attention to terms with low keyword difficulty but healthy traffic potential. If your competitors have thin content ranking for these terms, that’s your chance to produce something more in-depth and optimized.
Also, look for keyword gaps in secondary clusters. For example, if your competitor ranks for “best yoga mats” but not for “non-slip yoga mats for hot yoga,” you’ve just found a more specific angle with potentially lower competition.
This method works exceptionally well when combined with topical mapping. Instead of chasing isolated keywords, build content hubs where each piece connects and supports the others increasing topical relevance and boosting rankings across the cluster.
Find Hidden Gems with Location-Based and Geo-Specific Keywords

Geo-specific keywords combine local intent with niche topics, making them highly targeted and often low in competition.
These keywords usually contain city names, regions, or local qualifiers. For example, instead of targeting “digital marketing tips,” you could target “digital marketing tips for small businesses in Dallas.”
Local modifiers reduce competition significantly. Even if the search volume is lower, the conversion intent is usually much higher, especially for service-based businesses or localized content.
Use Google Trends to explore regional interest and see where demand is rising. Also try tools like BrightLocal or Google Keyword Planner set to specific locations to uncover localized terms your competitors might miss.
This strategy is effective not only for physical businesses but also for blog content that can be geo-tailored such as “best winter hiking trails in Colorado” or “affordable coworking spaces in Bangalore.”
Use Long-Tail and Question-Based Keywords for Easier Ranking

Long-tail keywords are longer and more specific phrases that users type when they’re closer to taking action or looking for precise answers.
According to a study by HitTail, long-tail keywords generate 70% of all web traffic. These keywords are usually less competitive because they serve a narrower audience but that’s also what makes them easier to rank for.
Tools like AnswerThePublic, AlsoAsked, and Google’s “People Also Ask” box are goldmines for long-tail queries. Phrases like “how to fix a leaky faucet without tools” or “best email marketing tool for non-profits” have clear intent, low competition, and a high chance of attracting the right visitor.
Make sure your content directly addresses these queries with relevant headings, clear formatting, and comprehensive answers. This improves your chances of appearing in featured snippets and other rich results.
Embedding long-tail and question-based keywords naturally into FAQs, H2 headings, and internal links further enhances your semantic relevance, helping Google understand the context of your content better.
Discover Low-Competition Keywords Through Competitor Analysis
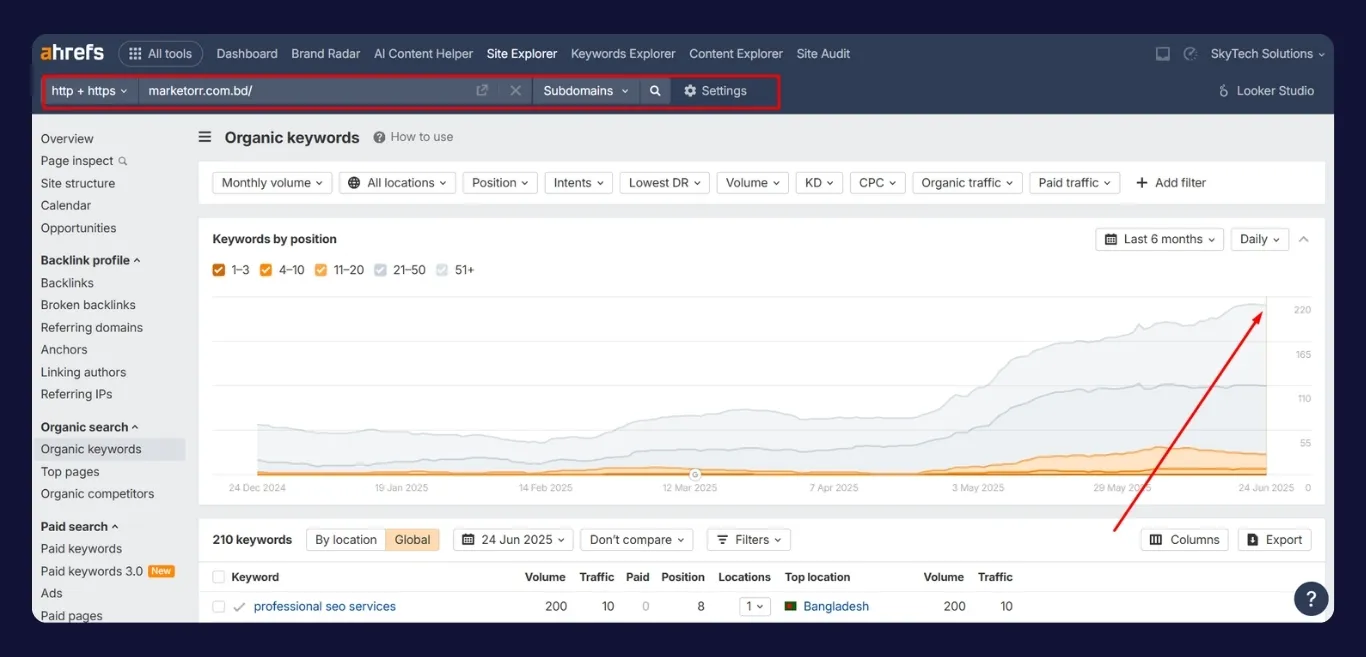
Analyzing competitors is one of the most effective ways to reverse-engineer success and find low-competition opportunities hidden in plain sight.
Begin by reviewing which pages drive the most organic traffic to your competitors using tools like Ahrefs’ Top Pages or SEMrush’s Organic Research. Look for posts or pages that are ranking without many backlinks or domain authority.
Open those URLs and check their keyword profile. Often, you’ll find terms with the lower competition that the content ranks for passively not even intentionally targeted.
Also, analyze how well the content aligns with user intent. If it only partially answers the query or lacks depth, you can create a better version by filling those gaps and improving structure, multimedia, and internal linking.
Don’t just focus on the top-performing content. Look at pages with declining traffic as well. If a keyword once ranked well but has dropped, it could indicate outdated content. Updating and targeting that keyword might offer a quick win if competition hasn’t yet surged.
Incorporate this competitive intelligence into your own topical strategy by not only covering the same keywords but expanding with semantically related ones and deeper subtopics.
How to Effectively Target Low-Competition Keywords
After identifying low-competition keywords, the next step is to target them with high-quality content that satisfies both user intent and search engine expectations. Execution is critical the right keyword alone won’t rank unless paired with a strategic content plan.
Optimizing Content for Keyword Relevancy and Authority
Keyword placement and semantic depth are key to helping search engines understand your content’s topic and relevance.
Integrate your main keyword naturally into your title, H1, URL, and meta description. But avoid overstuffing focus on clarity and user benefit. Sprinkle-related keywords and semantic phrases throughout the content to enhance context.
Use tools like Surfer SEO, NeuronWriter, or Clearscope to find relevant terms that often co-occur in top-ranking content. Including these semantically linked words helps Google connect your content with the topic cluster more accurately.
Don’t just answer the primary query. Go deeper. Cover related subtopics, include examples, add statistics, and incorporate visuals where needed. A comprehensive page reduces bounce rates and increases time on the page, both positive SEO signals.
Internal Linking Strategies for SEO Boost

Internal linking supports SEO by passing authority, improving crawlability, and reinforcing topical relevance between pages.
Every time you publish new content targeting a low-competition keyword, find related articles in your site and link to them, and vice versa. This creates a web of context that signals to Google your site is an authority on the subject.
Anchor text matters. Use descriptive, keyword-rich anchors that reflect the linked page’s topic. But vary them to avoid appearing manipulative. For example, use “beginner workout plans” in one link and “easy fitness routines” in another, both pointing to the same target page.
Also, use silo structures when building internal links. This means grouping related articles under broader parent topics and linking within those silos. It helps build a hierarchical structure that search engines can easily understand.
According to a study by NinjaOutreach, strategic internal linking can increase organic traffic by 40% within just a few months when applied consistently.
Leveraging Keyword Clusters for Topic Authority
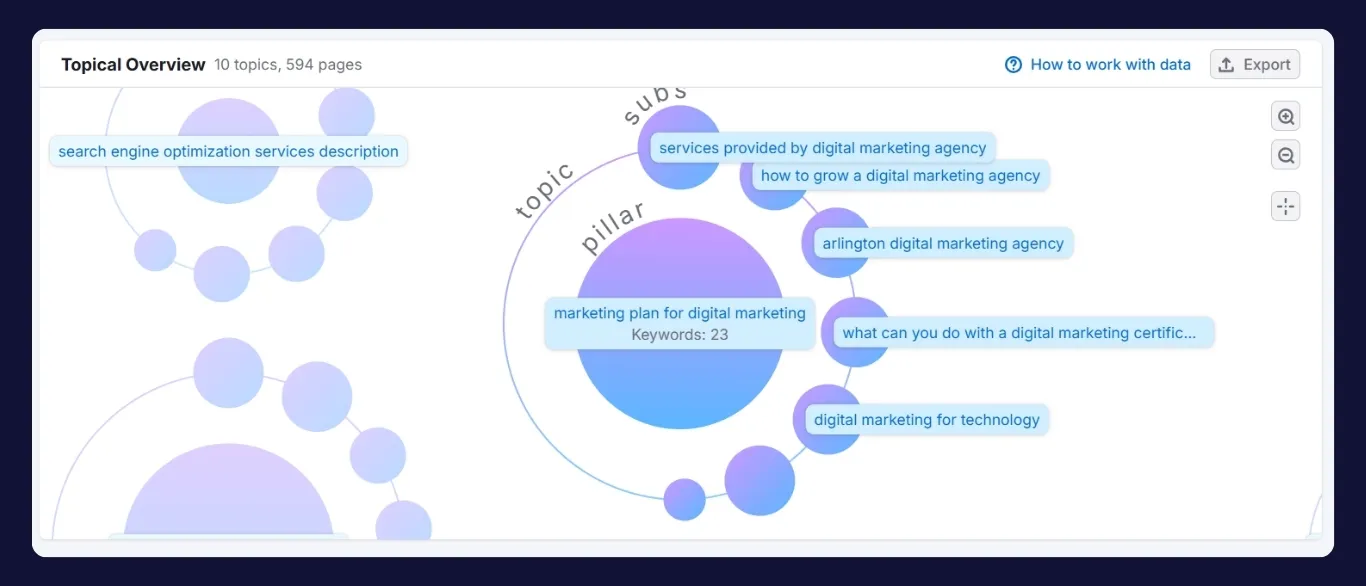
A single keyword doesn’t build authority but a cluster of related terms does. Keyword clustering means grouping semantically related keywords and covering them across multiple, interconnected pages.
For example, instead of writing one post on “low-competition keywords,” you’d also write supporting content like:
- How to Use Google Autocomplete for Keyword Research
- Tools for Finding Low-Competition Keywords
- Keyword Clustering Techniques for Beginners
- Long-Tail vs Short-Tail Keywords
Each of these links back to your main hub article and to each other, forming a strong topical cluster. This structure improves semantic relevance and builds a signal of authority over time.
Search engines reward comprehensive topical coverage because it improves user experience. When users find everything they need across your site, they stay longer and engage more to better rankings.
Should You Avoid High-Competition Keywords Completely?
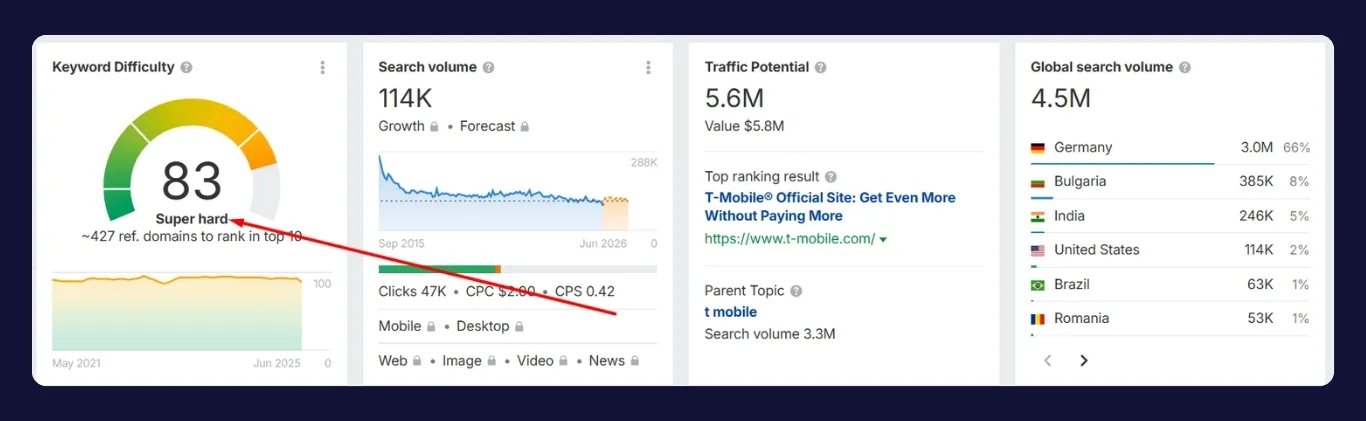
No, but your approach to them should be strategic and timed. While low-competition keywords are excellent for fast results and building authority, high-competition keywords still offer long-term value, especially once your site gains strength.
High-competition keywords often represent broad topics or commercial terms with significant search volume. Ranking for these can drive massive traffic, but the path is longer and requires more resources including high-quality backlinks, strong topical coverage, and established domain authority.
Instead of avoiding them completely, plan for them in your long-term strategy. Begin by supporting them through clusters of low-competition content that builds your site’s semantic relevance. As Google starts to associate your site with the broader topic, your chances of ranking improve even without directly targeting the most competitive terms from day one.
This technique is known as predictive topical authority. It involves preemptively building related content so that when you eventually target a high-competition keyword, your content is already contextually aligned and reinforced by surrounding pages.
Let your low-competition keywords bring traffic and authority first. Once you see consistent performance, use that foundation to go after broader and more competitive terms with greater confidence.
Final Thoughts
Finding and ranking for low-competition keywords isn’t just about shortcuts. it’s about smart SEO that aligns with how search engines work today. Google rewards relevance, intent matching, and topical depth, not just domain strength or backlink count.
By understanding search intent, analyzing competition carefully, and using keyword clustering, even newer websites can compete and thrive. Start small, but aim big. Every low-competition keyword you win adds a building block to your site’s authority.
Ready to grow your website Traffic? See how Marketorr’s expert SEO service ranks your website and increases organic customers. Explore our SEO solutions now!
Today

Md Rayhan Hossain is an SEO strategist with over 7 years of experience helping SaaS, service-based, and local businesses grow their visibility and revenue through search.
Before launching his own projects, Rayhan worked with agencies and in-house teams to lead successful SEO campaigns that combined strategic content, technical audits, and local optimization.
Over the years, he’s helped dozens of clients scale organic traffic and leads—especially in competitive niches—by using a mix of data-driven tactics and practical execution. His work has spanned everything from complex site migrations to ranking local businesses in tough markets.
Rayhan regularly shares field-tested SEO strategies on the Marketorr blog, where he breaks down what’s working in real-world client campaigns.


